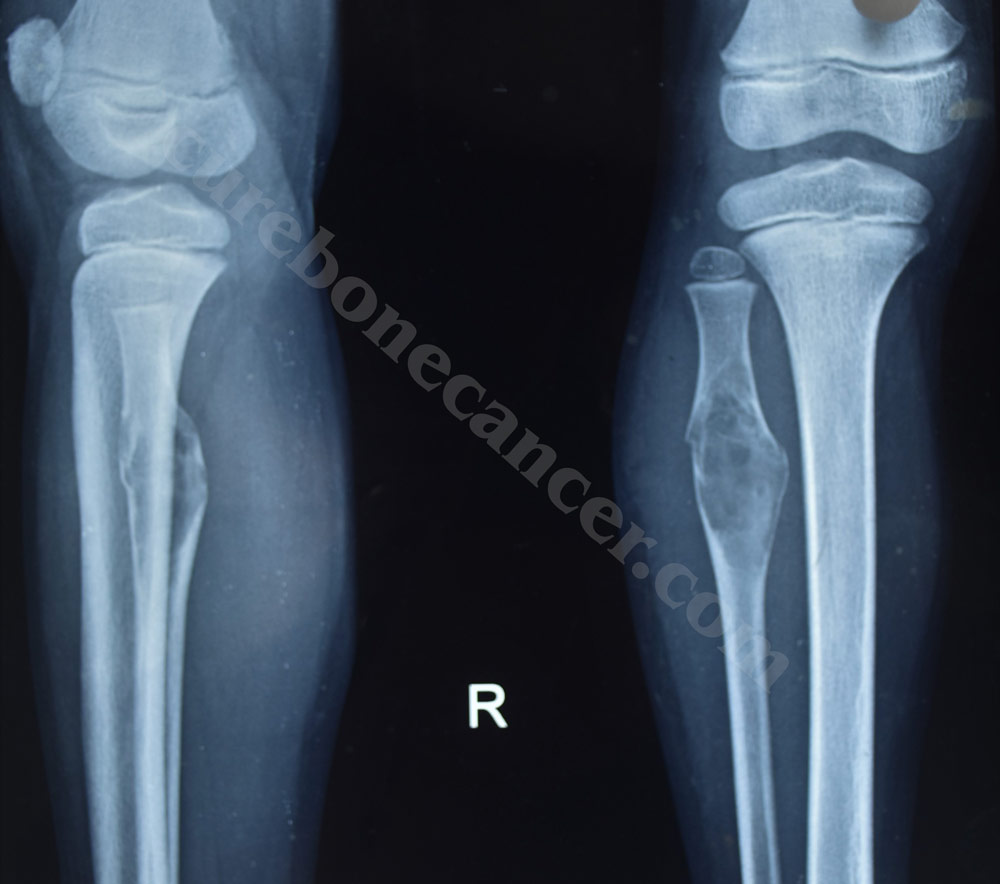
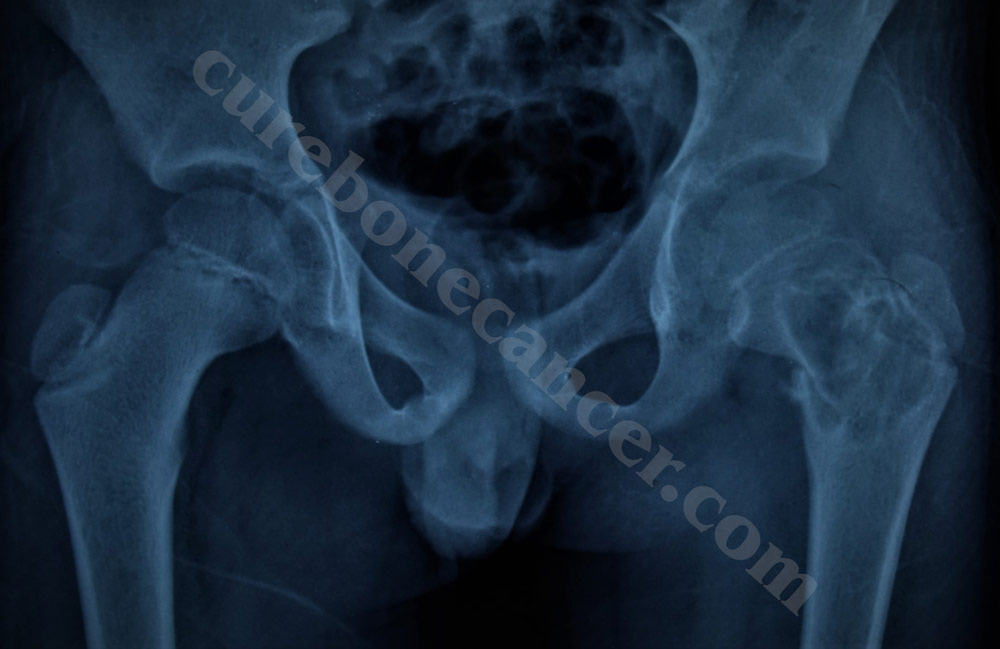
What is Aneurysmal Bone Cyst (ABC)?
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst (ABC) is a benign (Non Cancerous) cystic bone lesion. It consists of a multi loculated blood filled cavity within the bone. ABC can be primary when it arises de novo ( without any pre existing bone lesion) or secondary when it arises from a pre existing bone lesion ( like Giant Cell Tumour, Fibrous Dysplasia, Chondroblastoma etc.)
What causes ABC?
Though many theories have been proposed regarding the origin of ABC but local vascular disturbances within the bone has been widely accepted as the mechanism causing ABC. There is increased venous pressure and subsequent development of dilated and enlarged vascular bed within the affected bone. Lately, chromosome abnormalities have also been identified in patients of primary ABC.
What are symptoms of ABC?
Most commonly, it presents with pain in the affected bone which may be associated with swelling. It usually occurs in first 2 decades of life. Sometimes the patient may attribute the pain to any precedent trivial trauma (for example – fall while playing). The pain gradually worsens over time and may even result in pathological fracture of the bone.
How is ABC diagnosed?
After history and proper clinical examination, patient is subjected to X-rays and MRI. X-rays reveal well defined lytic lesions with septations. MRI typically shows fluid fluid levels, however, biopsy is the gold standard for the diagnosis.
What is biopsy? Who should do the biopsy?
In biopsy, some part of tumour tissue is removed and sent for examination under microscope. It can be open biopsy (in which a surgical incision is made to expose the tumorous bone and take out the diseased tissue) or a needle biopsy (in which a thin needle is used to take out the tissue without any incision). Since needle biopsy doesn’t involve any incision, the surgical trauma, pain and morbidity are lesser with needle biopsy.
One must also understand that needle biopsy is not synonymous with FNAC though both are done with a needle. FNAC has no role in the diagnosis of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst (ABC).
Since the location and technical aspects of biopsy can affect the treatment options and final outcome of the patient, biopsy should always be done by Orthopaedic Oncologist (specialist who treats bone and soft tissue tumours) or one of his team members.
We at Bone Cancer Clinic, Chandigarh do biopsy with a needle for almost all the cases.
How is ABC treated?
Sometimes , ABC can heal spontaneously after a pathological fracture. Aneurysmal Bone Cyst Treatment in India varies from minimally invasive modalities (minor surgery) like Curopsy, Sclerotherapy or a major surgery in the form of Extended curettage or a non surgical option like Angioembolisation or a combination of these modalities depending on the extent of the lesion, location of the lesion etc.
Here, at Cure Bone Cancer Clinic, Chandigarh, treatment is customised for each patient and usually minimally invasive modalities are tried first in majority of the patients.
What is Curopsy?
Curopsy is “Biopsy with Intention to cure”. In this technique, a bone biopsy needle is inserted into the lesion under C-arm (X-ray) guidance and the cavity is scrapped so as to damage the lining of the cyst. The trauma so inflicted has shown to cause healing. The material so obtained during curopsy is sent to the pathologist for analysis.
What is Sclerotherapy?
In sclerotherapy, first a bone biopsy needle is inserted into the lesion so as to break all the septa and damage the lining of the cyst and then a sclerosant (Polidocanol) is injected in to the cavity under C-arm guidance. The sclerosant damages the lining and causes healing of the lesion
Dr Rajat Gupta
Orthopaedic Oncologist
Bone Cancer Clinic
# 5, Sector 19 A, Chandigarh
https://goo.gl/maps/KT5hkxsRVy12
SCO 141 (Backside), Sector 14, Panchkula
https://goo.gl/maps/aLdmMwMqvMumVXe76